Intelligent Order Routing: KIBO OMS’s Fulfillment Optimization
Legacy order management systems with static routing rules can't handle modern retail demands. Learn how intelligent order routing transforms fulfillment operations.
Legacy Order Logic Meets a Modern Commerce Reality
The commerce battlefield has shifted. Today’s customers expect near-instant delivery, real-time product availability, and frictionless transitions across channels — from mobile to store to doorstep and back. Retailers are under relentless pressure to meet these expectations while optimizing costs and adapting to constant supply chain disruptions.
Yet the backbone of many fulfillment operations — the Order Management System (OMS) — is still stuck in an earlier era. Static routing rules, batched inventory updates, and brittle logic persist in systems never designed for modern omnichannel fulfillment operations. These outdated platforms are no longer just a technical liability but a strategic risk.
This blog is for executive decision-makers — CIOs, VPs of Fulfillment, and Heads of Omnichannel —responsible for aligning fulfillment operations with modern business goals. In the following sections, we’ll explore:
- The systemic pitfalls of static, rules-based OMS platforms
- The rise of intelligent order routing as a strategic imperative
- How modern platforms like KIBO OMS outperform legacy systems
- The measurable, business-wide impact of adopting dynamic fulfillment logic
The Fulfillment Reality Gap: What Legacy OMS Can’t Deliver
Retail has evolved into a landscape where agility is essential. Consider the realities:
- Shoppers demand same-day or two-day delivery, not vague “5-7 business day” windows.
- Buy Online, Pick Up In Store (BOPIS) and ship-from-store are table stakes, not novelties.
- Brands must fulfill from multiple locations — warehouses, stores, drop-ship vendors — all in real time.
- Returns are part of the brand experience, not just a post-purchase headache.
Most legacy OMS platforms, however, were built to handle centralized, warehouse-based fulfillment and basic transactional logic. They struggle to orchestrate the complex, real-time decisioning modern retail requires.
“An OMS that doesn’t provide near‑real‑time inventory availability just won’t cut it anymore.” — Forrester Wave™: Order Management Systems, Q1 2025
“The combination of adding sales channels and fulfillment locations… is breaking legacy OMS systems.” — Gartner Market Guide: Distributed Order Management.
Five Structural Failures of Static, Rules-Based OMS
Let’s examine the five most critical limitations of rules-bound OMS architecture and why they are incompatible with today’s demands.
1. Rigid Logic That Can’t Adapt
Hardcoded routing rules — like “if customer is in the West, ship from DCA” — are inflexible. These rules can’t pivot in real time when stockouts, weather disruptions, or labor shortages arise. Teams resort to manual overrides or expensive workarounds, degrading operational efficiency and customer experience.
2. Siloed Inventory Visibility
Legacy systems rely on batched updates and siloed inventory views. They lack a unified picture of stock across stores, warehouses, in-transit shipments, and third-party partners. This fragmentation leads to overselling, missed sales, and inaccurate available-to-promise (ATP) data.
3. Cost-Ignorant Fulfillment Decisions
Rules-based OMS typically optimizes for speed or proximity — not cost. For example, a system might prioritize shipping from the closest DC, even if it’s far more expensive due to labor or carrier rates. Without real-time evaluation of total landed cost, retailers leak margin on every order.
“Retailers with legacy OMS have seen profitability suffer due to the much higher variable cost of fulfilling ecommerce orders without intelligent optimization.” — KIBO
4. Lack of Scalability
Adding fulfillment nodes or sales channels to a rules-based OMS creates complexity quickly. Each change often requires new logic or system integrations, leading to bloated rule sets, brittle configurations, and expensive technical debt. Scaling to new markets or fulfillment strategies becomes slow and risky.
5. Fragmented Returns and Post-Purchase Visibility
Bolt-on systems or manual processes often handle returns. Agents lack end-to-end visibility. Refunds get delayed. Returned items are routed inefficiently. These inefficiencies aren’t just cost sinks — they erode customer loyalty and inflate reverse logistics costs.
The Shift to Intelligent Order Routing: From Logic to Learning
The modern OMS doesn’t follow rigid scripts. It acts like a decision engine, evaluating real-time data to choose the best omnichannel fulfillment path for each order. This includes not just inventory and proximity but also cost, capacity, service level agreements (SLAs), and customer preferences.
KIBO OMS exemplifies this next-generation approach. Rather than relying on static rules, it uses strategy-based configurations, ranking and filtering logic, and cost-based sourcing algorithms — all operating dynamically and modifiable by business users without writing new code.
“OMS leaders offer distributed order management capabilities that evaluate all sourcing options dynamically — optimizing for cost, speed, and profitability.” — Forrester Q1 2025 OMS Evaluation.
“In today’s market, milliseconds and pennies at scale make the difference — OMS is now a driver of margin and brand trust.” — McKinsey & Company.
Side-by-Side Comparison: Legacy vs. Intelligent OMS
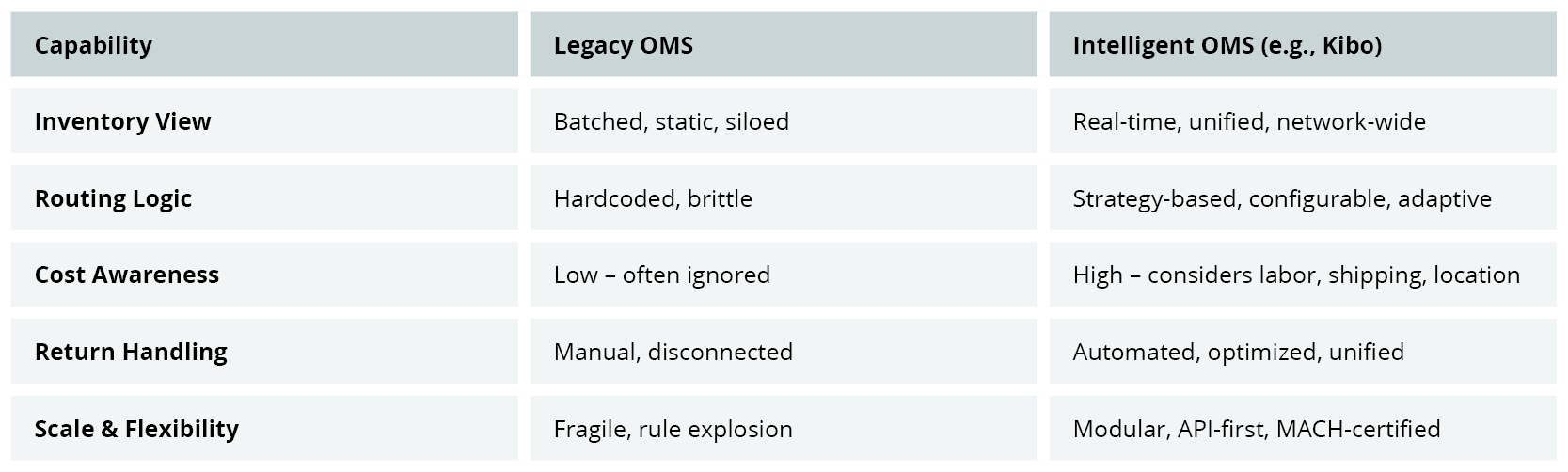
Strategic Advantages of Intelligent Order Routing (with Kibo OMS)
KIBO OMS replaces rigid, hardcoded rules with a flexible, intelligence-augmented engine that responds dynamically to real-world conditions. The benefits span every layer of the retail fulfillment network.
1. Network-Wide Inventory Coordination
Retailers using KIBO gain an accurate, real-time view of inventory across every node — stores, DCs, suppliers, and in-transit locations. This visibility powers more innovative sourcing and better fulfillment decisions.
Rather than defaulting to a warehouse, KIBO might route an order to a local store with the item in stock, optimizing for speed and cost. This enables high-value omnichannel offerings like endless aisle, BOPIS, and ship-from-store — all while maximizing inventory turns and minimizing splits.
According to KIBO, retailers using this unified view have increased inventory utilization by up to **15%**.
2. Cost-Optimized Fulfillment Logic
KIBO OMS evaluates the complete cost profile of each fulfillment node before assigning an order: carrier rates, labor costs, inventory carrying costs, and SLAs are factored in dynamically. This ensures orders are routed not only quickly, but profitably.
Instead of shipping from a distant DC to meet a delivery promise, the system might consolidate fulfillment at a nearby store with idle capacity, reducing transportation costs and warehouse handling simultaneously.
Retailers leveraging KIBO’s cost-based routing logic have reported 12–18% reductions in shipping cost per order, while preserving delivery SLAs.
3. Smarter, Connected Reverse Logistics
Unlike legacy OMS, which treats returns as an afterthought, KIBO integrates reverse logistics into the same intelligent orchestration engine.
Returned items are routed to where they can be most effectively resold — whether that’s the originating store, a DC needing replenishment, or a store with local demand. This allows businesses to recapture revenue faster, reduce return shipping costs, and simplify refund processing.
Agents also benefit from real-time visibility across the return journey, enabling proactive service and streamlined customer experiences — a critical component in building post-purchase loyalty.
4. Enablement of D2C, Dropship, and Hybrid Fulfillment Models
KIBO’s composable architecture empowers retailers and brand manufacturers to support a wide range of fulfillment scenarios from a single platform:
- Direct-to-consumer orders from brand DCs or third-party retailers
- Dropshipping from vendors based on availability or proximity
- Subscription-based fulfillment logic (e.g., recurring shipments)
- Pop-up and seasonal fulfillment centers with minimal setup
Because every node can be configured as a fulfillment location — and governed by business logic, not code — brands can launch new strategies quickly without reengineering backend systems.
As a MACH-certified platform, KIBO OMS integrates flexibly with external systems and grows modularly, enabling iterative modernization at the pace of business⁵.
5. Real-Time Resiliency and Operational Agility
In today’s volatile environment, omnichannel fulfillment strategies must adapt in real time. With KIBO, retailers can automatically re-route orders if a node goes offline, a carrier hits capacity, or a regional weather event disrupts delivery.
The platform can also redistribute fulfillment load across stores based on staffing levels, operational capacity, or real-time demand — minimizing bottlenecks during peaks and improving SLA performance without manual intervention.
This built-in adaptability reduces reliance on safety stock and emergency labor, empowering businesses to respond instantly to disruptions without impacting customer expectations.
Strategic Business Impact: OMS as a Competitive Weapon
An intelligent OMS is not just an IT upgrade. It is a foundational investment in customer experience, revenue growth, and margin resilience.
Elevating the Customer Experience
Real-time inventory visibility, intelligent promise accuracy, and seamless fulfillment choices lead to fewer canceled orders and faster deliveries — all of which directly enhance brand trust and loyalty.
46% of shoppers check product availability online before visiting a store. — Ignitiv
With accurate ATP data and agile fulfillment logic, retailers meet expectations and create brand-differentiating experiences.
Accelerating Revenue Growth
Intelligent OMS logic directly improves top-line results by activating store inventory for ecommerce, enabling endless aisle scenarios, and minimizing cart abandonment through better delivery options.
Furthermore, by reducing failed deliveries and missed sales due to stockouts or misrouting, retailers capture revenue that static OMS logic would have forfeited.
Delivering Operational Efficiency
Intelligent orchestration cuts costs across the fulfillment chain:
- Lower transportation costs through better sourcing
- Fewer manual interventions and rework
- Balanced workload across fulfillment locations
It also enables automated exception handling, reducing call center volume and speeding up resolution times.
“OMS modernization is no longer an IT decision — it’s a margin strategy.” — Accenture Retail Tech Outlook, 2025
Supporting Scalability and Future-Readiness
KIBO’s API-first, cloud-native architecture ensures organizations can scale, adapt, and innovate — without rewrites or downtime. Whether expanding to new regions, adding fulfillment nodes, or launching a new commerce channel, the system is designed to evolve with the business.
“The future of OMS is modular — platforms that evolve with your business, not slow it down.” — Forrester Analyst Emily Pfeiffer¹
Executive Call to Action: Lead the Shift
Static OMS logic belongs to a static era. The modern retail enterprise must move from rigid routing to intelligent orchestration — from guesswork to real-time decisioning.
With intelligent platforms like KIBO OMS, the operational backend becomes a source of agility, profitability, and competitive edge. The gains are tangible, and the need is urgent.
It’s time to ask:
- Is your OMS optimizing for cost and service — or just executing old rules?
- Can it pivot dynamically during disruptions — or do you rely on firefighting?
- Does it enable your future business models — or hold them back?
Executive Checklist
- Conduct a routing logic audit: Are your rules fit for modern demand?
- Assess inventory visibility: Can you promise what you don’t see?
- Benchmark your shipping cost per order: Are you leaving margin on the table?
- Evaluate modular, AI-augmented OMS platforms: Is your architecture ready for what’s next?
Final Word
It’s time to move beyond static rules and let intelligence drive your fulfillment.
Retailers who modernize their OMS today will reduce costs, delight customers, and outpace the competition.
Don’t let legacy systems hold you back — the future of retail belongs to the agile.
Sources
Gartner – Market Guide: Distributed Order Management
Kibo Commerce – Cost-Based Order Optimization Overview (kibocommerce.com)
McKinsey – Retail Technology 2025: Driving Profit Through Automation
Kibo Commerce – Composable Commerce & MACH Certification
Ignitiv – OMS and Inventory Accuracy in Omnichannel Retail (ignitiv.com)
Accenture – Retail Tech Outlook 2025
Forrester – Wave Report: Order Management Systems, Q1 2025 (forrester.com)

Rama Aluri
Practice Leader, E-commerce, Enterprise Content Management, and Application Services
Published September 11, 2025


